Abstract
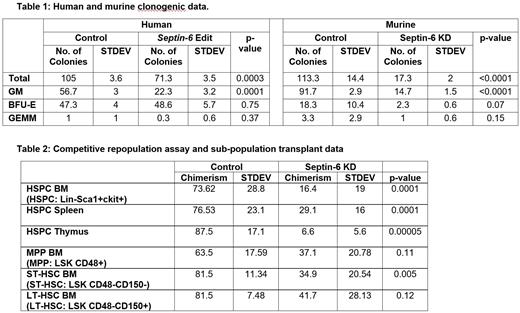
Septin family proteins are key regulators of cytoskeletal organization and cytokinesis although little is known about their function in normal hematopoiesis. Septins are implicated in T and B cell lymphomas; and acute myeloid leukemias, where they frequently act as fusion partners with the Mixed-Lineage Leukemia (MLL) gene. Previously, we identified a non-syndromic newborn with severe neutropenia which progressed to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) (Renella et al. AJH, 2022). Next-generation sequencing revealed a novel X-linked germline mutation in the SEPTIN-6 gene associated with dysmyelopoiesis (SEPTIN6 c.1282T>C); and a second stop-gain somatic mutation hypothesized to rescue hematopoietic function, but the mechanism of MDS was not defined. Based on our initial publication, a second patient with neutropenia/MDS has since been identified in Seattle with a mutation in the same codon (SEPTIN6 c.1282T>A) suggesting an important new molecular mechanism for pediatric MDS. Both identified patients had a high degree of myeloid tetraploidy in the marrow and were refractory to G-CSF. To assess the pathobiology of the published patient's mutation, we replicated the germline T>C mutation using single base-pair gene editing in normal donor primary CD34+ cells. Editing rates were ~50-70%. Morphological studies demonstrated that SEPTIN-6 edited human CD34+ cells demonstrated enlarged, multi-nucleated and dysplastic nuclei. These findings were similar to the appearance of the patient's bone marrow myeloid precursor cells. These edited cells also demonstrated a decline in clonogenic activity notably with a selective reduction in granulocyte-macrophage (GM) colonies (Table 1). Both myeloid and erythroid colonies showed a reduction in colony size. These data directly confirm an important role for this mutated SEPTIN-6 in abnormal hematopoietic function.
The septin-6 family of proteins consist of septin-6, 8, 10, 11 and 14 which may have overlapping functions in cells. Murine single cell mRNA expression data demonstrate that hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) express significant levels of Septin-6, Septin-11 and 8, with little to no expression of Septin-10 and 14. To better understand the functional role of Septin-6, we created lentivirus vectors tagged with a GFP reporter that contained shRNAs against Septin-6. Culture of Septin-6 knockdown (Septin-6 KD) murine HSPC in IMDM (10ng/ml IL-3, 25ng/ml of SCF, TPO, Flt-3 and IL-6) resulted in an average of 18-fold decrease in cell counts compared to controls (p=0.02). This was accompanied by an increase in cell cycle: S-phase: Septin-6 KD 55.7%; controls 42.5%, p=0.05 and a cumulative decrease in the G0/G1 and G2/M phase suggesting that Septin-6 is important in regulating cell cycle in HSPC. Controls were a non-targeting shRNA and an empty vector for all experiments described. Furthermore, knockdown of Septin-6 caused a decrease in total clonogenic activity with defects seen in both myeloid (GM) and erythroid (BFU-E) colonies (Table 1). Competitive repopulation assays, wherein transduced BoyJ HSPC (GFP+ Septin KD and BFP+ control were mixed 1:1) were injected into lethally irradiated C57Bl/6 mice, demonstrated a reduction in multilineage chimerism in the peripheral blood, bone marrow, spleen and thymus in primary and secondary transplant recipients after knockdown of Septin-6 (Table 2). To better define function in specific hematopoietic populations of HSPC, we performed knockdown in FACS-sorted purified cells. Engraftment studies demonstrated a significant reduction in bone marrow chimerism in primary transplant recipients after knockdown of Septin-6 most clearly in ST-HSC (Table 2) with a trend towards a decrease in LT-HSC and MPP. These data support a key role of Septin-6 in murine and human hematopoiesis via alterations in cell cycle and validate the pathogenic nature of a specific mutation in human SEPTIN-6.
Disclosures
Camargo:Fog Pharmaceuticals: Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Williams:Bluebird: Consultancy, Other: Provides Vector; Chief Scientific Chair, Emerging Therapy Solutions: Consultancy; Scientific Advisory Board, Skyline Therapeutics: Consultancy; Insertion Site Analysis Advisory Board, Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Scientific Advisory Board, Beam Therapeutics: Consultancy; Orchard Therapeutics: Other: Provides vector; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Steering Committee (fees donated to NAPAAC); Insertion Site Advisory Board, Biomarin: Consultancy; Novartis: Other: Provision of study materials, medical writing.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal